This door monitor project uses an infrared beam to monitor door & passageways or any other area. When the beam is broken a relay is tripped which can be used to sound a bell or alarm. Suitable for detecting customers entering a shop, cars coming up a driveway, etc. The IR beam is very strong. Distances over 25 feet can be monitored. A 12V DC supply is required to power the circuit. A 12V wall adaptor is fine.
Provision has been made so that only one power supply needs to be used to power both units. The relay is rated to switch mains voltages.
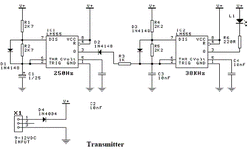
The charge time (output high) is given by:
THIGH = 0.693 x R1 x C1 (or 0.693 x R4 x C3)
The discharge time (output low) is given by:
TLOW = 0.693 x R2 x C1 (or 0.693 x R5 x C3)
The output frequency = 1 / (THIGH + TLOW)
The output from the IC1 is coupled via diode D2 and resistor R3 to the ‘trigger’ input of IC2. When the IC1 output is low it stops IC2 from running and IC2’s output is forced high (no IR LED current). When IC1 output is high, IC2 runs and the IR LED is pulsed at 38KHz.
The Waitrony IR LED is driven directly from the output of IC2. Resistor R6 sets the maximum LED current. With a 12VDC supply the current is about 45mA (the LED drops 2V across it when conducting). Lowering the value of R6 will increase the current through the LED thus boosting the signal strength. This may be necessary if the kit is used outside in direct sunlight or if you need “very long range”. Keep in mind that the maximum current that the 555 can handle is 200mA
If the distance to be monitored is less than about 10 yards then you will need to fit the 5mm shrink tubing over the IR LED. This narrows the radiating angle of the IR beam and makes it much more directional. The IR output is strong. It can easily bounce off walls etc to give false readings.
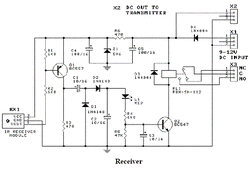
The output of RX1 is the 250Hz signal from the transmitter. This signal is passed via transistor Q1, capacitor C1and diode D2 to capacitor C2. C2 is fully charged during the high portion of the signal. It starts to discharge during the low portion of the signal via LED L1, resistor R4 and transistor Q2. However the discharge time is much longer than the off time of the signal so the voltage across C2 is always enough to keep transistor Q2 on and therefore the relay operated.
When the beam is broken the output of RX1 is high. Transistor Q1 is off and capacitor C2 is no longer being recharged. It will eventually discharge to the point where transistor Q2 will turn off and the relay will release. The “turn off” delay is determined by the time constant of resistor R5 and capacitor C3. With the values used it is approx. half a second.
Capacitor C1 prevents a steady DC voltage on the collector of Q1 from charging C2. This would occur if the beam was not present or the beam was a continuous 38kHz signal. In other words, the receiver module will only respond to a pulsed 38kHz signal.
LED L1 gives a visual indication when the IR beam is present and is used to help with installation and setup. Zener diode Z1, resistor R6 and capacitor C4 provides a stable 5.6V supply for the IR module. The relays used should be mains rated: 250V/12A; 120VAC/15A
 RSS Feed
RSS Feed